Having solved more than 1500 LeetCode problems, if there is one thing I have learned, it’s this:
LeetCode is less about the number of problems you have solved and more about how many patterns you know.
Learning patterns enable you to solve a wide variety of problems in less time and help you quickly identify the right approach to a problem you have never seen before.

In this article, I’ll walk you through the 15 most important patterns I learned that made my LeetCode journey lot less painful.
I’ll share when to use each pattern along with a sample problem and provide links to LeetCode problems you can practice to learn these patterns better.
1. Prefix Sum
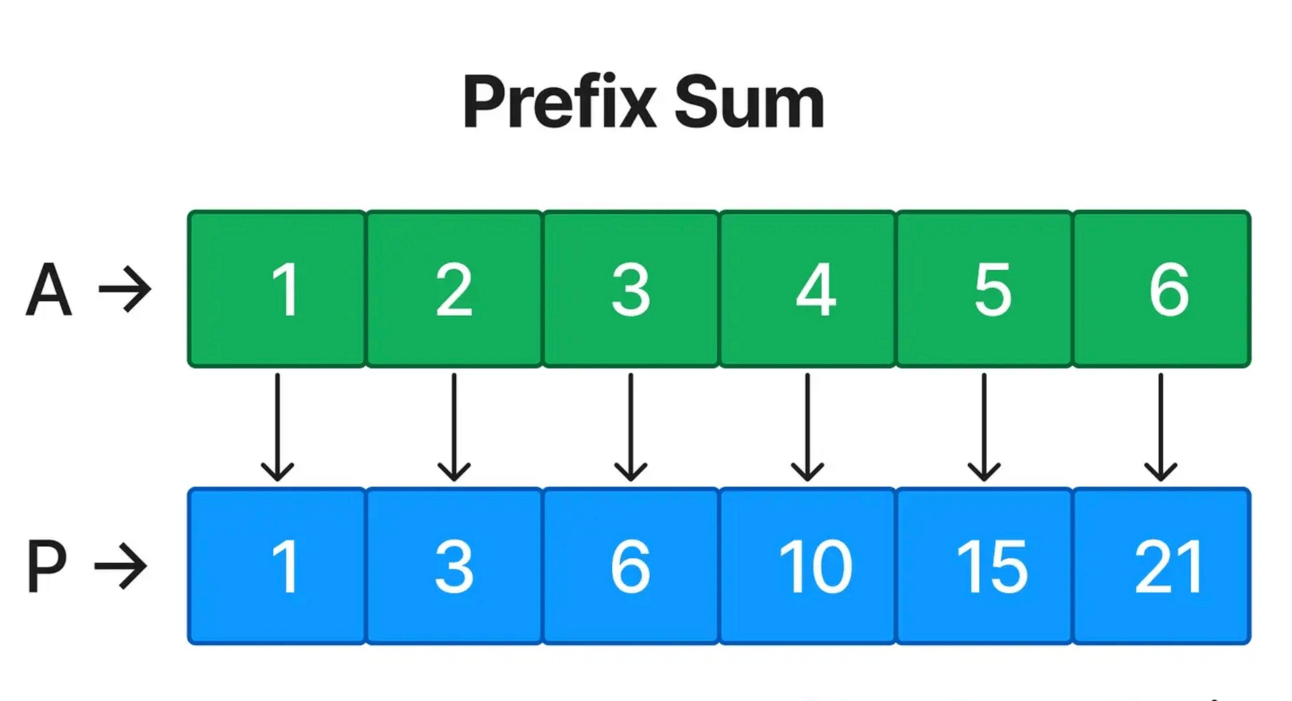
Prefix Sum involves preprocessing an array to create a new array where each element at index i represents the sum of the array from the start up to i. This allows for efficient sum queries on subarrays.
Use this pattern when you need to perform multiple sum queries on a subarray or need to calculate cumulative sums.
Sample Problem:
Given an array nums, answer multiple queries about the sum of elements within a specific range [i, j].
Example:
Input:
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],i = 1,j = 3Output:
9
Explanation:
Preprocess the array
Ato create a prefix sum array:P = [1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21].To find the sum between indices
iandj, use the formula:P[j] - P[i-1].
LeetCode Problems:
2. Two Pointers

The Two Pointers pattern involves using two pointers to iterate through an array or list, often used to find pairs or elements that meet specific criteria.
Use this pattern when dealing with sorted arrays or lists where you need to find pairs that satisfy a specific condition.
Sample Problem:
Find two numbers in a sorted array that add up to a target value.
Example:
Input:
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 6],target = 6Output:
[1, 3]
Explanation:
Initialize two pointers, one at the start (
left) and one at the end (right) of the array.Check the sum of the elements at the two pointers.
If the sum equals the target, return the indices.
If the sum is less than the target, move the left pointer to the right.
If the sum is greater than the target, move the right pointer to the left.
LeetCode Problems:
3. Sliding Window

The Sliding Window pattern is used to find a subarray or substring that satisfies a specific condition, optimizing the time complexity by maintaining a window of elements.
Use this pattern when dealing with problems involving contiguous subarrays or substrings.
Sample Problem:
Find the maximum sum of a subarray of size k.
Example:
Input:
nums = [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2],k = 3Output:
9
Explanation:
Start with the sum of the first
kelements.Slide the window one element at a time, subtracting the element that goes out of the window and adding the new element.
Keep track of the maximum sum encountered.
LeetCode Problems:
4. Fast & Slow Pointers
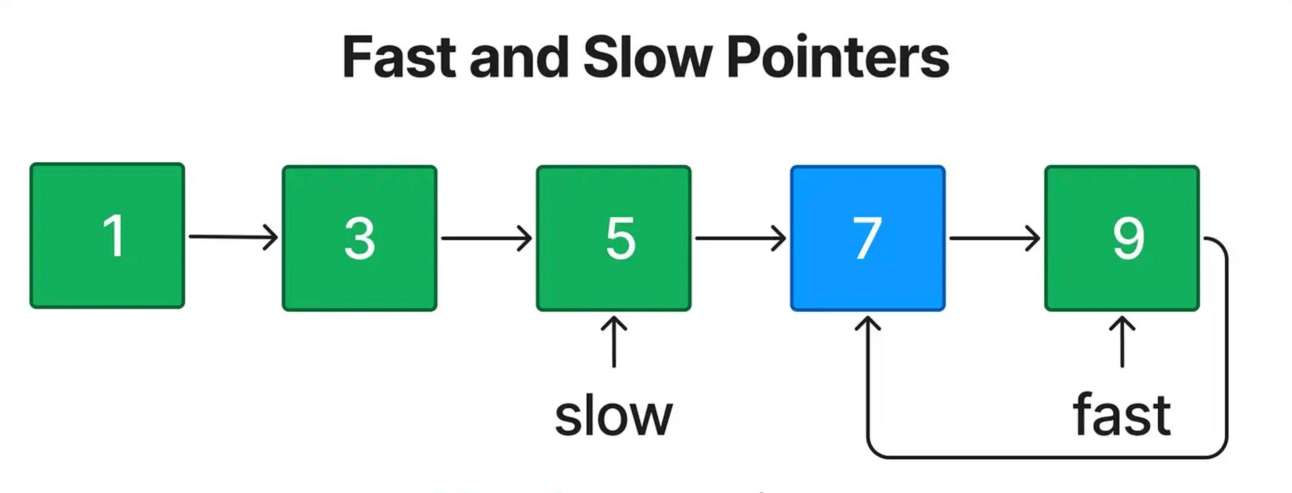
The Fast & Slow Pointers (Tortoise and Hare) pattern is used to detect cycles in linked lists and other similar structures.
Sample Problem:
Detect if a linked list has a cycle.
Explanation:
Initialize two pointers, one moving one step at a time (slow) and the other moving two steps at a time (fast).
If there is a cycle, the fast pointer will eventually meet the slow pointer.
If the fast pointer reaches the end of the list, there is no cycle.
